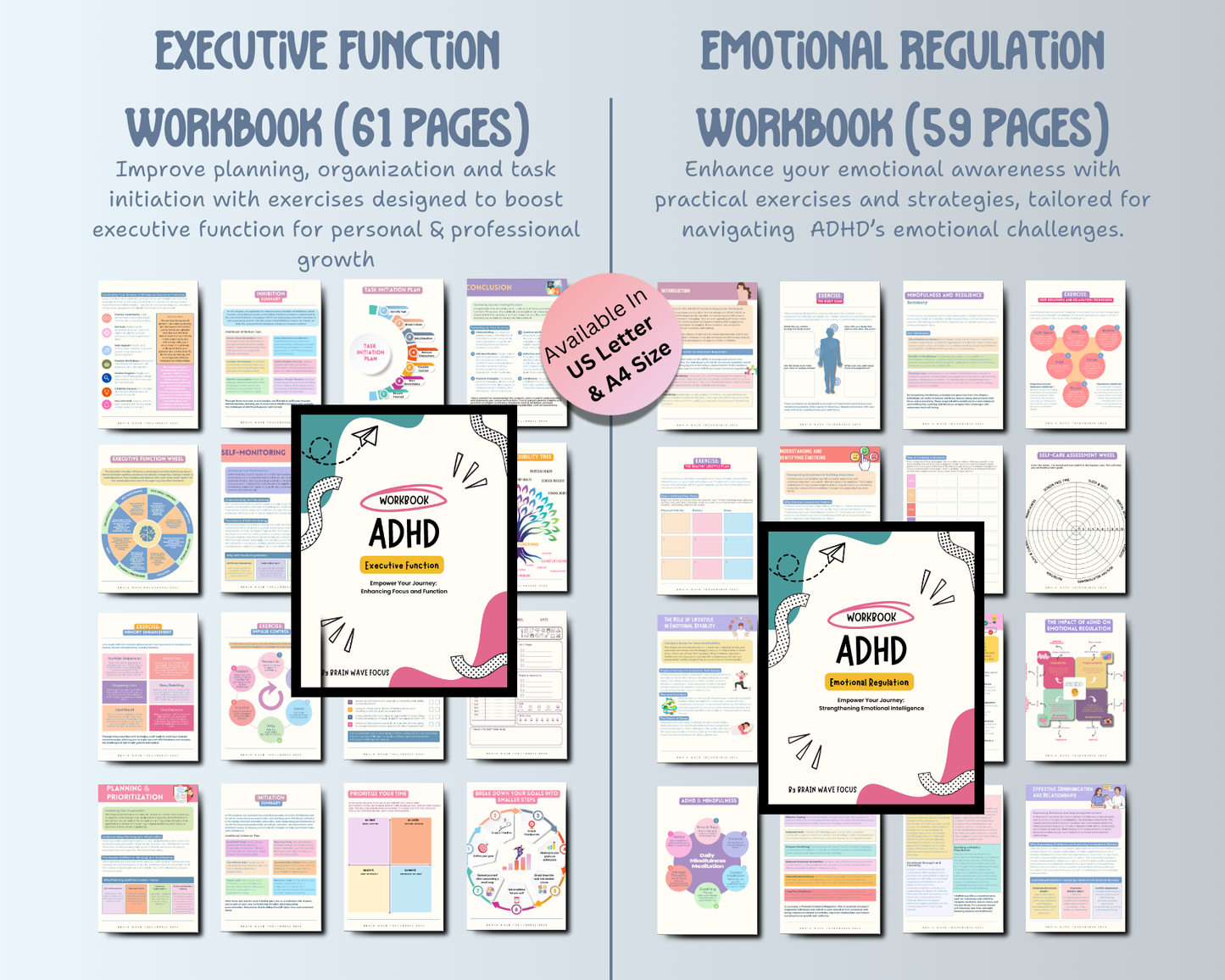
Living with ADHD can bring a unique set of challenges, and one of the lesser-known struggles many experience is Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria (RSD). RSD is an intense emotional response to real or perceived rejection, criticism, or disappointment. For those with ADHD, RSD can lead to overwhelming feelings of sadness, anger, or shame, which can be hard to control or understand. Let's dive into what RSD is, how it affects people with ADHD, and strategies that can help manage it.
What Is Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria?
The term "dysphoria" means a state of unease or dissatisfaction, and "rejection sensitivity" refers to an extreme sensitivity to rejection or criticism. RSD isn’t just about feeling disappointed or sad when things don’t go as planned; it’s a sudden, intense reaction to feeling rejected or judged. This can lead to a strong emotional response that often feels disproportionate to the situation, lasting from minutes to hours.
For people with ADHD, RSD can sometimes feel like a sudden wave of intense emotions that are hard to control. RSD episodes may be triggered by criticism, social rejection, or even perceived failure. It's not unusual for someone experiencing RSD to feel a deep sense of inadequacy or self-doubt, which can lead them to avoid situations where rejection might occur.
How RSD Affects People with ADHD
People with ADHD often have heightened emotional sensitivity, and RSD can intensify this. Here are a few ways RSD affects those with ADHD:
- Avoidance of Social Situations: Fear of rejection can make people with ADHD avoid social or work situations where they might be judged, criticized, or rejected. This avoidance can lead to social isolation and limit opportunities.
- Strained Relationships: RSD can cause misunderstandings and conflicts in personal relationships. Since people with RSD may overreact to minor comments or gestures, they may struggle to maintain stable relationships.
- Perfectionism: Many with RSD try to avoid criticism by striving for perfection, leading to feelings of constant pressure. Unfortunately, this perfectionism is often unattainable, creating a cycle of disappointment and self-blame.
Tips for Managing RSD in ADHD
While there is no specific cure for RSD, several strategies can help manage its effects:
- Mindfulness and Self-Awareness: Practicing mindfulness can help individuals recognize when RSD is being triggered. By becoming aware of these patterns, they can learn to distance themselves from intense emotional reactions.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help reframe negative thought patterns and provide tools to manage intense emotions. Many people with ADHD find CBT helpful in reducing the impact of RSD.
- Medication: Some medications that treat ADHD can also help lessen RSD symptoms. Stimulant medications, for example, can reduce impulsivity and emotional sensitivity, making it easier to manage RSD reactions.
- Support Networks: Having a support network of friends, family, or mental health professionals can help provide perspective and reassurance, especially during emotionally intense episodes.
RSD is a significant aspect of ADHD that deserves more awareness and understanding. With the right strategies, people with ADHD can work toward managing the intense feelings that come with RSD, leading to healthier relationships and a more balanced emotional life.